Prerevolutionary Moscow
Moscow has been called the Third Rome by a clergyman who with this name
compared it to Rome and Constantinople, both as the centres of big empires
and as strongholds of Christianity.
This boast overlooks the fact that Christianity didn’t enter Russian
soil through Moscow, but through Kiev, and Moscow only "inherited"
this self- appointed role after the destruction of the first Russian empire
to be, the Kievian Rus, in 1240. During the centuries of Mongolian dominion
(the "yoke", as it is called in Russia) on Russian soil many
small city states/principalities existed, fighting against each other,
often with the assistance of Mongolian leaders, who practised the principle
"Divide and rule!" Among these city states Moscow with time
rose to primacy and the Muscovite Grand Dukes took over the task of reuniting
the Russian lands, until one of them, Ivan IV, "the Terrible"
was crowned the first "Tsar of all Rus" in 1547.
 |
The church of the Ascension at Kolomenskoye. The village of Kolomenskoye was once a residence of the Grand Dukes and Tsars. Nowadays it’s a museum site for 16-17th century architecture, situated in the southern part of Moscow. |
|
The buildings in Kolomenskoye belong to the oldest buildings left in Moscow. In former times most Russian buildings, whether houses, or palaces, or churches were from wood and therefore didn’t survive till today.
The church of the Ascension was built in 1532 to celebrate the birth of Ivan the Terrible. It was one of the first stone churches of Russia and has a unique architecture. To me it seems to resemble a rocket. A prophecy for the Soviet space program? And it’s even called church of the Ascension, so they had an idea of where it should go to! |
 |
Slavic settlement in the Moscow area, according to traces
left by the first settlers, started in the 11th century. By then the Kievian
Rus had been in existence for a while and its Grand Dukes had already
converted to Christianity with Vladimir Svatoslavich in 988.
Moscow was first mentioned in a chronicle in 1147. It developed as a trading
centre at the connection of the Moskva, Neglinnaya and Yauza rivers. It
was also destroyed by the Mongolian invaders in 1238 but quickly recovered.
By numerous wars, sieges and battles it gained an extension of territory
and independence from the Mongolian khans in the course of the rule of
the Grand Dukes Daniil (1276-1303), Ivan Kalita (1328-1341), Dmitri Donskoy
(1362-1389), Ivan III. (1462-1505) and Vassili III. (1505-1533).
 |
Columns and stairs of the church of the Ascension |
Other principalities, as the ones of Novgorod, Tver, Rostov and Pskov were incorporated into the Muscovite territory. The Mongolian yoke was thrown off when the Muscovite Grand Dukes felt strong enough to refuse to pay the tribute.
|
The 17th century gate through which one enters
the area of Kolomenskoye.
|
 |
Under the rule of Ivan IV. "the Terrible" the Mongolians – in Russian referred to as Tartars – were finally defeated and no longer constituted a threat to Russian rulers. Trade relations were established with Western countries through the port of Kholmogory, nowadays Arkhangelsk, on the White Sea. The conquest of Siberia started. After a time of unrest (the "smuta") Russia defeated attempts of Poland to impose its rule and even its catholic faith on Russia. Russia emerged again as a Great power in the time of Peter I (the Great) and after its victory in the battle of Poltava in the Nordic War against Sweden finally gained access to the Baltic Sea which led to the foundation of a new capital, Saint Petersburg.
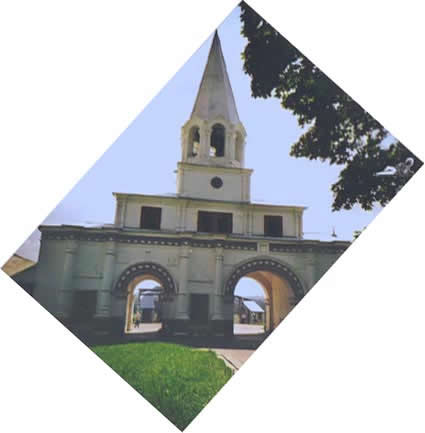 |
This gate is called the Red Gate, though it’s not red at all. Either it was painted red in former times, or, more likely, it was once called the "beautiful gate", being the main gate to the tsarist estate. The name of the Red Square has the same origin: The word for "red" in modern Russian in former times meant "beautiful". |
| Water tower (17th century) and Saint George’s bell tower (16th century) in Kolomenskoye. |  |
The Moscow Empire had to fight real enemies in the course
of its ascent: Tartars/Mongolians, Lithuanians, the German Knights’
Order, Sweden, and it succeeded in battle and administration.
Moscow, as a city and for a long time the centre of an empire, ideologically
had to fight more sophisticated rivals. For a long time, and to a certain
extent till today, it has to fight the phantom of the Kievian Rus.
 |
The church of the Saviour in the Spaso-Andronikov monastery, built in the 15th century. The monastery is known for having housed the most famous Russian icon painter, Andrei Rublyov. There are alledgedly paintings from him inside the church, but when I was there the building was closed and wasn’t in good shape. |
The Muscovites became the "Great Russians", the guardians of Orthodoxy and Russian political unity, the Ukrainians became the "Small Russians" and an unimportant province in the great Russian Empire. This derogatory point of view persisted in Bolshevik policies during the prerevolutionary times and soviet policy after the takeover of the Communist Party. In the peace of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet Republic easy-mindedly ceded the Ukraine to Germany and Austria, as they had little support there, anyhow.
|
A lesser well-known church in the district of Khamovniki, on the Komsomolski Prospect: the Church of Saint Nikola.
It stems from the 17th century, when Khamovniki was a "Posad", a settlement of craftsmen, not having the status of a town, but still enjoying a certain exemption from serfdom. As this Posad was a weaver’s settlement, this church is also known as the "Weavers’ Church"
|
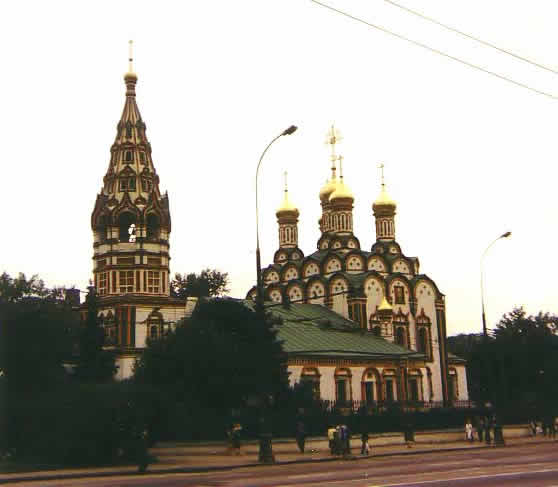 |
The tower to the left is the bells’ tower which in Russia was always built apart from the church as it had to fulfil different tasks from the church itself: It had to be more stable, and was exposed to the heavy vibrations of the very heavy bells.
The building between the church and the bell tower, with the green roof, was erected in the 80-ies, in a style cooresponding to the other buildings, perhaps for the housing of the parish priest, of for a school. It is remarkable that in socialist times the authorities tried to adjust somehow to the building’s style as well as to the necessities it wanted to meet.
|
The Novodevichy Convent
|
The only other rival after Kiev Moscow had to face was Petersburg after Peter I decided to put his capital there, as a "Window to the West". For about 200 years Moscow had to play second fiddle, always envious of the role of the pretender to the throne that it considered its own. The main force clinging to Moscow was the old nobility, the Boyars, whom already Ivan the Terrible had stripped of some of their power, attempting to replace them by a class of "new nobles", the "court’s men", as the nobles are called nowadays.
|
Ivan the Terrible, as painted by Viktor Vasnyetsov (who lived some centuries later, so the painting has more to be seen as a result of the artist’s imagination than of Ivan’s real appearance ...)
The first Russian Tsar has definitely left his brand on Moscow’s architecture and perhaps on Russian political culture. His spirit still lingers in the city. He was a very well-read man, and had a large library that he hid before his death. It has never reappeared, and once in a while people set out to find it – so far in vain. |
 |
It is an irony of fate that the traditional role as Russia’s capital was restored to Moscow by the Bolsheviks. After the victory of the October Revolution the new politicians realised that their program wasn’t too popular within the Western Imperialist countries. The latter supported – openly or secretly – various counterinsurgent armies and inflicted a four-year long civil war on revolutionary Russia. For these reasons the Bolshevik leaders decided to transfer the capital of their new state to a less exposed and vulnerable part in the spring of 1918. So Moscow was given back its glory and importance, while Petersburg was stripped of it.
Moscow has been a barrier to dictators of Western Europe. Napoleon took Moscow, but this was the beginning of his defeat. The German army in 1941 got so close that they could see the church towers of Moscow, but with an enormous effort and great loss of life, and the help of the climate Moscow was saved from capture. And in the end the Nazi Empire was defeated in Russia, a fact that has been neglected in the decades of the Cold War ...